- The Writer Playbook
- Posts
- The $5 Trillion Shortcut: How the Panama Canal Redefined Global Trade
The $5 Trillion Shortcut: How the Panama Canal Redefined Global Trade
The Panama Canal, a $5 trillion trade lifeline, redefined global commerce through innovation and sacrifice. From French failure to U.S. success, it overcame deadly challenges, geopolitical tensions, and environmental risks, symbolizing humanity's relentless ambition and the cost of progress.
The $5 Trillion Shortcut: How the Panama Canal Redefined Global Trade
At first glance, the Panama Canal appears to be a serene waterway connecting two great oceans. But beneath its calm waters lies a tale of extraordinary ambition, a staggering $5 trillion trade flow, and a history steeped in blood, betrayal, and breathtaking innovation. This man-made marvel doesn’t just connect the Atlantic and Pacific—it connects the past, present, and future of global commerce.
The French Failure: A $300 Million Catastrophe
In the late 19th century, French engineer Ferdinand de Lesseps—hailed as the visionary behind the Suez Canal—sought to replicate his success by creating a canal through Panama. Investors poured $300 million into the project (equivalent to over $9 billion today), convinced it would revolutionize global trade. But they underestimated the ferocity of the Panamanian jungle.
As described in [Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914], the challenges were insurmountable. Tropical diseases like malaria and yellow fever killed over 22,000 workers. The unforgiving terrain swallowed equipment whole. The project collapsed in 1889, leaving de Lesseps disgraced and investors bankrupt.
The dream of a canal was buried—at least for a time.
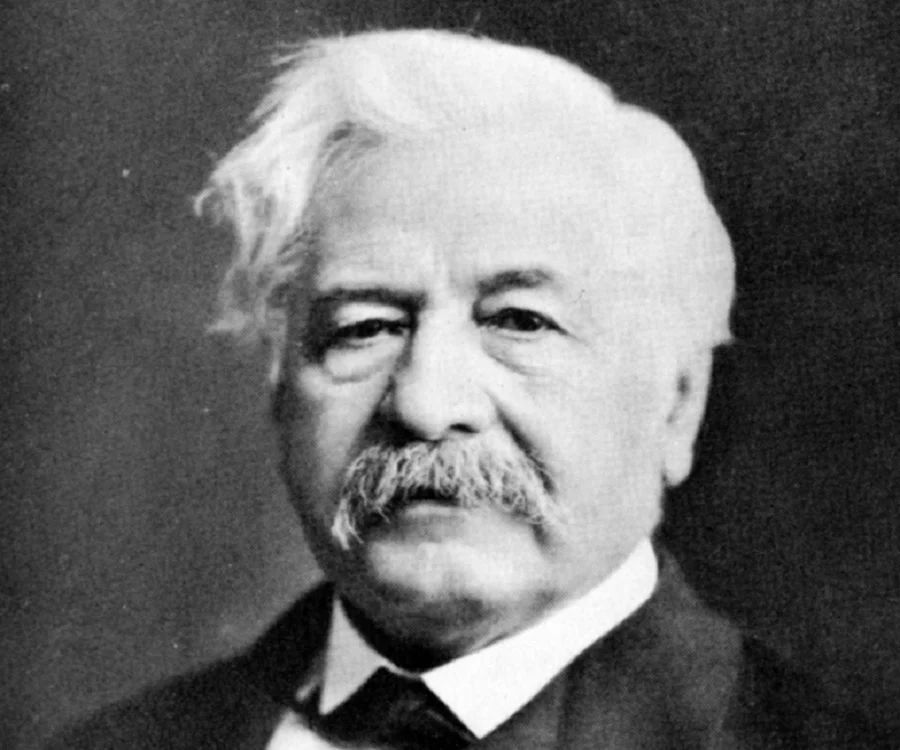
-Ferdinand de Lesseps, the visionary behind the Suez Canal, faced devastating failure in Panama, where dreams of a sea-level canal were swallowed by disease and terrain
America’s $40 Million Gamble: Taming the Jungle
By the early 20th century, the United States saw an opportunity to step in. Under President Theodore Roosevelt, the U.S. purchased the failed French project for $40 million. Roosevelt declared the canal critical to America’s economic and military dominance, famously stating, “I took the Isthmus.”
The U.S. faced the same challenges as the French: a jungle teeming with disease, treacherous mountains, and a climate that seemed determined to thwart progress. But they had something the French didn’t—innovative thinking.
William C. Gorgas, a pioneering doctor, launched a revolutionary sanitation campaign. By draining swamps and eradicating mosquitoes, he eliminated yellow fever in the canal zone. Meanwhile, engineers led by John Frank Stevens and later George Washington Goethals reimagined the canal’s design. Instead of a sea-level canal, they built a series of locks that lifted ships over the Isthmus of Panama.
As detailed in [The Big Ditch: How America Took, Built, Ran, and Ultimately Gave Away the Panama Canal], the U.S. invested $375 million (equivalent to $10 billion today). It was a Herculean effort, involving 56,000 workers, 60 million pounds of dynamite, and the excavation of 268 million cubic yards of earth.
By 1914, the Panama Canal opened, shaving 8,000 miles off the journey between New York and San Francisco. It was a triumph—but not without cost. Over 5,600 workers died during the American phase of construction, and Panama’s sovereignty was overshadowed by U.S. control of the canal.
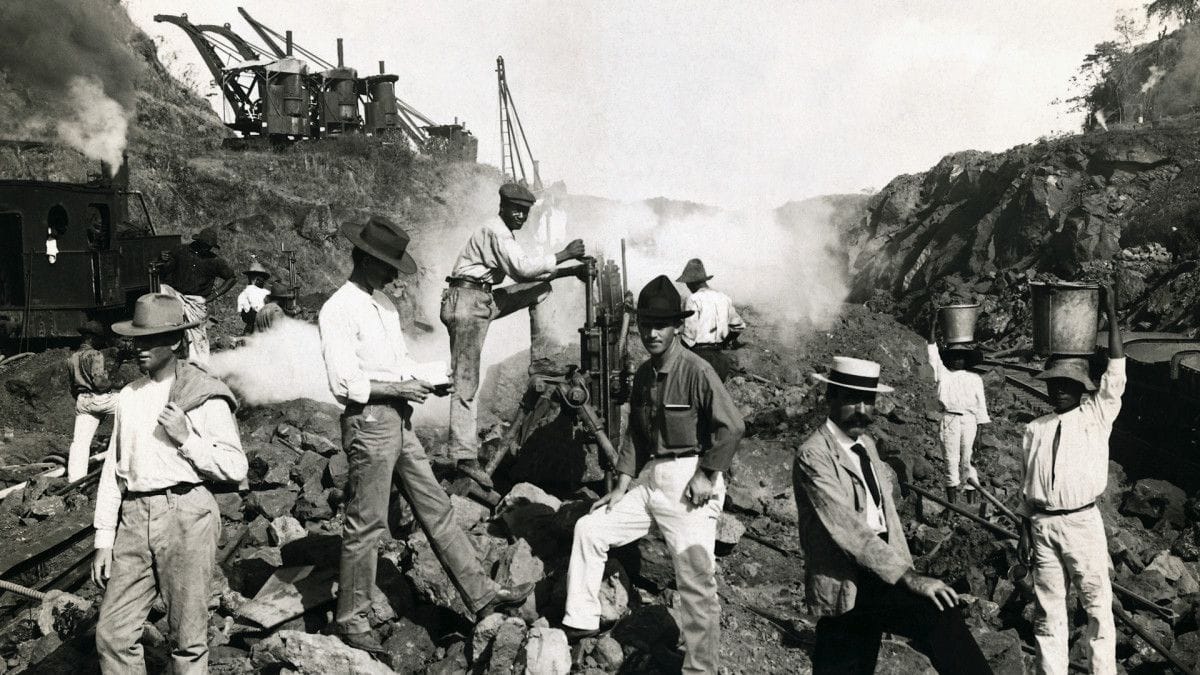

-Workers toiling under unforgiving conditions during the construction of the Panama Canal in the early 1900s.
A $5 Trillion Trade Lifeline
Today, the Panama Canal is one of the most lucrative trade routes in the world. More than 12,000 ships pass through its locks annually, carrying over $5 trillion in goods. The canal connects 140 maritime routes and 1,700 ports, making it the backbone of global commerce.
Every ship that transits the canal pays a toll, which can range from $800 for small vessels to over $1 million for mega-ships. In 2022 alone, the canal generated over $3 billion in revenue for Panama.
Yet, as [The Canal Builders: Making America’s Empire at the Panama Canal] highlights, this prosperity didn’t come without conflict. For decades, Panamanians protested U.S. control of the canal, arguing that it symbolized colonial exploitation. After years of negotiations, the U.S. handed over control to Panama in 1999—a moment of national pride and sovereignty.
Geopolitical Tensions and Environmental Challenges
In the 21st century, the Panama Canal remains at the center of global geopolitics. China has invested heavily in Panama’s infrastructure, sparking concerns in Washington about Beijing’s growing influence. The canal’s strategic location makes it a pawn in the chess game of global power.
But the canal faces a more immediate threat: climate change. Rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall have caused water shortages, endangering the canal’s ability to operate at full capacity. The canal depends on rain-fed lakes to function, and as droughts become more severe, its future hangs in the balance.
Expansions in 2016 added a third set of locks to accommodate larger ships, increasing its capacity by 50%. Yet, even this modernization cannot shield the canal from the dual threats of environmental instability and increasing competition from other trade routes, such as the Arctic.
The Price of Progress
The Panama Canal stands as a testament to human ingenuity and resilience. It reshaped the world economy, connecting East and West like never before. But its legacy is also a stark reminder of the cost of ambition: tens of thousands of lives lost, billions of dollars spent, and entire ecosystems disrupted.
As detailed in [Path Between the Seas], the canal is more than just a waterway—it’s a symbol of what humanity can achieve when it dares to dream big, and what it must remember when chasing progress.
Conclusion: A Waterway of Power and Possibility
The Panama Canal is not just a marvel of engineering—it’s a story of human determination, a $5 trillion artery of trade, and a battleground for power and survival. Its history reminds us that progress is never easy, but the rewards can be transformative.
The question remains: as the world changes, will the Panama Canal continue to hold its place as the lifeline of global trade? Or will it become a relic of a bygone era?
One thing is certain: the canal’s story is far from over.
Disclaimer: Some of the links in this newsletter are affiliate links, meaning I may earn a small commission if you choose to purchase through them—at no additional cost to you. These recommendations are based on research and aim to provide you with valuable insights. Thank you for supporting my work!